Table of Contents
Financial investment firms invest money on part of their customers who, in return, share in the earnings and losses.

Investment firm do not include brokerage firm firms, insurer, or financial institutions. In United States safety and securities policy, there are at least five types of investment firm: As a whole, each of these investment firm must register under the Securities Act of 1933 and the Financial Investment Business Act of 1940. A fourth and lesser-known sort of investment firm under the Investment Business Act of 1940 is a Face-Amount Certificate Company.
A major kind of business not covered under the Investment Firm Act 1940 is private investment firm, which are just exclusive companies that make investments in stocks or bonds, but are restricted to under 250 financiers and are not regulated by the SEC. These funds are often composed of really well-off financiers.
Managed funds typically have constraints on the kinds and quantities of financial investments the fund manager can make. The bulk of investment companies are common funds, both in terms of number of funds and properties under administration.
Investment Management servicing Arlington
The first investment company were developed in Europe in the late 1700s by a Dutch investor that intended to allow tiny capitalists to pool their funds and expand. This is where the idea of investment firm come from, as stated by K. Geert Rouwenhorst. In the 1800s in England, "investment merging" emerged with depends on that resembled contemporary mutual fund in framework.
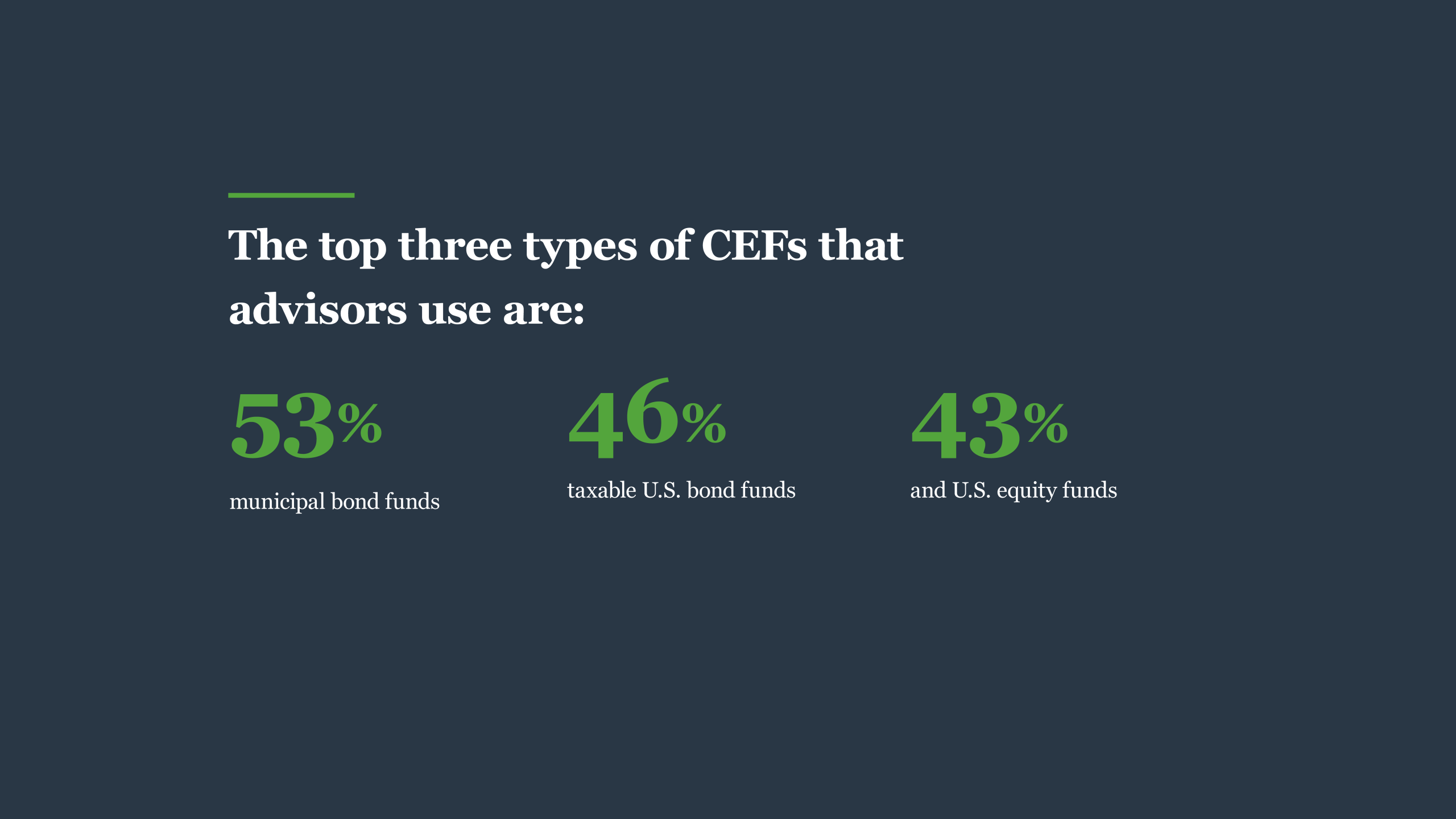
The 1929 supply market crash and Wonderful Anxiety momentarily hindered mutual fund. New protections guidelines in the 1930s like the 1933 Securities Act brought back investor self-confidence. A number of technologies then brought about steady development in investment firm possessions and accounts over the years. The Investment Firm Act of 1940 manages the framework and operations of investment companies.
In 1938, it authorized the creation of self-regulatory companies like FINRA to look after broker-dealers. The Securities Act of 1933 needs public securities offerings, including of investment firm shares, to be signed up. It also mandates that financiers get a current program describing the fund. "Investment firm". U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Investment Firms
Lemke, Lins and Smith, Regulation of Financial Investment Firms, 4.01 (Matthew Bender, 2016 ed.). Chaudhry, Sayan; Kulkarni, Chinmay (2021-06-28). "Style Patterns of Spending Apps and Their Effects on Investing Actions". ACM. pp. 777788. doi:10.1145/ 3461778.3462008. ISBN 978-1-4503-8476-6. "Financial investment Clubs and the SEC",, Modified January 16, 2013. (PDF). Financial Investment Company Institute. 2023.
In retail mutual fund, countless financiers may be entailed by means of intermediaries, and they may have little or no control of the fund's activities or knowledge concerning the identifications of other capitalists. The possible number of investors in a private mutual fund is normally smaller sized than retail funds. Exclusive mutual fund often tend to target high-net-worth individuals, including politically subjected persons, and fund supervisors may have a close relationship with their client financiers.
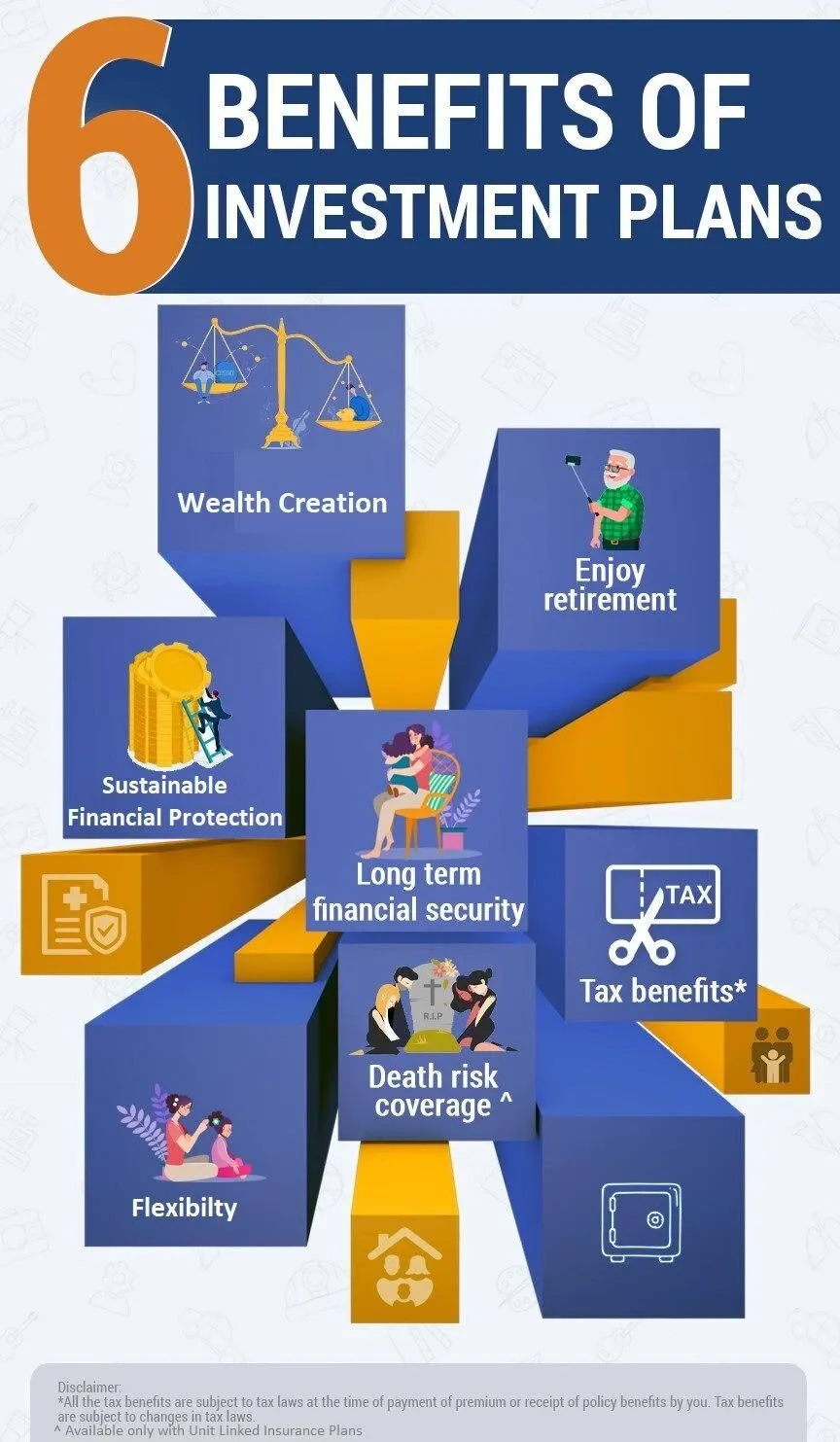
Passive funds have been expanding in their market share, and in some territories they hold a significant part of possession in openly traded firms. There are many various categories for financial investment funds. Some are closed-end, implying they have a fixed number of shares or funding, whilst others are open-end, suggesting they can grow right into unlimited shares or resources.
The rates, risk, and terms of derivatives are based on a hidden asset, and they enable investors to hedge a placement, rise take advantage of, or guess on a property's modification in worth. A financier might own both a stock and a choice on the exact same supply that enables them to sell it at an established rate; as a result, if the stock's price drops, the option still keeps value, decreasing the investor's losses.
Whilst taken into consideration, provided the focus of this briefing on the BOT of corporate lorries, a full therapy of the useful ownership of properties is outside its extent. A financial investment fund works as a channel to gain from several assets being held as investments. Financiers can be people, business vehicles, or organizations, and there are typically a variety of middlemans between the capitalist and financial investment fund along with between the mutual fund and the underlying economic properties, specifically if the fund's units are exchange-traded (Box 1).
Investment Company in Arlington
Depending on its legal form and framework, the people exercising control of a financial investment fund itself can vary from the people who have and take advantage of the underlying properties being held by the fund at any type of offered moment, either straight or indirectly. Both retail and personal financial investment funds typically have fund supervisors or advisors that make financial investment choices for the fund, selecting safeties that align with the fund's goals and take the chance of tolerance.
and act as middlemans in between investors and the fund, promoting the trading of fund shares. They attach capitalists with the fund's shares and carry out professions on their part. manage the registration and transfer of fund shares, preserving a record of shareholders, processing ownership changes, and issuing proxy products for investor conferences.
Navigation
Latest Posts
Investment Company
Mineral Rights Companies
Bathroom Remodel Price